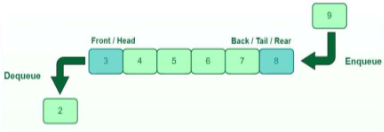
Queue
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle.
It operates like a line where elements are added at one end (rear) and removed from the other end (front).
⭐Queue - Array Implementation:
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Queue {int front, rear, size;int *arr;public:Queue(int s) {front = rear = -1;size = s;arr = new int[s];}// Enqueue operationvoid enqueue(int value) {if (rear == size - 1) {cout << "Queue is full" << endl;return;}else{if(front == -1){front = 0;}rear++;arr[rear] = value;}}// Dequeue operationvoid dequeue() {if (front == -1 || front > rear) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}else{cout << "Dequeued: " << arr[front] << endl;front = front + 1;}}// Peek operationvoid peek() {if (front == -1 || front > rear) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}else {cout << "Front element is: " << arr[front];}}// Display operationvoid display() {if (front == -1 || front > rear) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}else{cout << "Queue Elements are: ";for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++)cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;}};int main() {Queue q(5);q.enqueue(10);q.enqueue(20);q.enqueue(30);q.display();q.dequeue();q.display();q.peek();return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Queue Elements are: 10 20 30
Dequeued: 10
Queue Elements are: 20 30
Front element is: 20
⭐Queue - Linked List Implementation:
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;struct Node {int data;Node* next;};class Queue {Node *front, *rear;public:Queue() {front = rear = nullptr;}// Enqueue operationvoid enqueue(int value) {Node* temp = new Node();temp->data = value;temp->next = nullptr;if (rear == nullptr) {front = rear = temp;}else {rear->next = temp;rear = temp;}}// Dequeue operationvoid dequeue() {if (front == nullptr) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}Node* temp = front;front = front->next;if (front == nullptr){rear = nullptr;}int removed = temp->data;delete temp;cout << "Dequeued: " << removed << endl;}// Peek operationvoid peek() {if (front == nullptr) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}cout << "Front element: " << front->data << endl;}// Print operationvoid print() {if (front == nullptr) {cout << "Queue is empty\n";return;}cout << "Queue elements are: ";Node* temp = front;while (temp != nullptr) {cout << temp->data << " ";temp = temp->next;}cout << "\n";}};int main() {Queue q;q.enqueue(10);q.enqueue(20);q.enqueue(30);q.print();q.dequeue();q.print();q.peek();return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Queue elements are: 10 20 30
Dequeued: 10
Queue elements are: 20 30
Front element: 20
⭐Queue – Operations:
- Enqueue() - Insertion of elements to the queue.
- Dequeue() - Removal of elements from the queue.
- Peek() - Acquires the data element available at the front node of the queue without deleting it.
- isFull() - Validates if the queue is full.
- isNull() - Checks if the queue is empty.
⭐Priority Queue:
- A priority queue is a type of queue that arranges elements based on their priority values
- Elements with higher priority values are typically retrieved before elements with lower priority values.
- Priority queue can be implemented using the following data structures:
- Arrays
- Linked list
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;struct Node {int value;int priority;Node* next;};Node* head = nullptr;// Insertionvoid insert(int value, int priority) {Node* newNode = new Node();newNode->value = value;newNode->priority = priority;newNode->next = nullptr;if (head == nullptr || head->priority < priority) {newNode->next = head;head = newNode;}else {Node* current = head;while (current->next != nullptr && current->next->priority >= priority) {current = current->next;}newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;}}// Deletion (removes the highest priority element)Node deleteMax() {if (head == nullptr) {cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;return {-1, -1, nullptr};}Node* temp = head;Node deleted = {head->value, head->priority, nullptr};head = head->next;delete temp;return deleted;}// Traversalvoid traverse() {if (head == nullptr) {cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;return;}Node* current = head;while (current != nullptr) {cout << "(" << current->value << ", " << current->priority << ") ";current = current->next;}cout << endl;}int main() {insert(10, 2);insert(30, 3);insert(20, 1);insert(40, 5);cout << "Priority Queue after insertions: ";traverse();Node deleted = deleteMax();cout << "Deleted max: (" << deleted.value << ", " << deleted.priority << ")" << endl;cout << "Priority Queue after deletion: ";traverse();return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Priority Queue after insertions: (40, 5) (30, 3) (10, 2) (20, 1)
Deleted max: (40, 5)
Priority Queue after deletion: (30, 3) (10, 2) (20, 1)
⭐Difference between Priority Queue and Normal Queue:
- There is no priority attached to elements in a queue, the rule of first-in-first-out(FIFO) is implemented whereas, in a priority queue, the elements have a priority.
- The elements with higher priority are served first.
⭐Deque (Double-ended Queue):
- A double-ended queue (deque) is an abstract data type that generalizes a queue, for which elements can be added to or removed from either the front or rear.
- An input-restricted deque:
- It is one where deletion can be made from both ends, but insertion can be made at one end only
- Output-Restricted Deque:
- It is a deque with some limitations while performing deletion operations
- Four basic operations are performed on deque, they are as follows:
- Insertion at Rear
- Insertion at Front
- Deletion at Front
- Deletion at Rear
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Global variables for dequeint* arr;int front = -1;int rear = 0;int currentSize = 0;int capacity;// Function to insert an element at the frontvoid insertFront(int value) {if (currentSize == capacity) {cout << "Deque is full!" << endl;return;}front = (front + 1) % capacity;arr[front] = value;currentSize++;if (rear == 0) {rear = front;}}// Function to insert an element at the rearvoid insertRear(int value) {if (currentSize == capacity) {cout << "Deque is full!" << endl;return;}rear = (rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity;arr[rear] = value;currentSize++;if (front == -1) {front = rear;}}// Function to delete an element from the frontvoid deleteFront() {if (currentSize == 0) {cout << "Deque is empty!" << endl;return;}front = (front - 1 + capacity) % capacity;currentSize--;if (currentSize == 0) {front = -1;rear = 0;}}// Function to delete an element from the rearvoid deleteRear() {if (currentSize == 0) {cout << "Deque is empty!" << endl;return;}rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;currentSize--;if (currentSize == 0) {front = -1;rear = 0;}}// Function to display the deque elementsvoid display() {if (currentSize == 0) {cout << "Deque is empty!" << endl;return;}cout << "Deque elements: ";for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {cout << arr[(front - i + capacity) % capacity] << " ";}cout << endl;}int main() {capacity=5;arr = new int[capacity];insertRear(10);insertRear(20);insertFront(30);display();deleteFront();display();insertFront(40);insertRear(50);display();deleteRear();display();return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Deque elements: 30 10 20
Deque elements: 10 20
Deque elements: 40 10 20 50
Deque elements: 40 10 20
🚨Thanks for visiting finenotes4u✨
Welcome to a hub for 😇Nerds and knowledge seekers! Here, you'll find everything you need to stay updated on education, notes, books, and daily trends.
💗 Bookmark our site to stay connected and never miss an update!
💌 Have suggestions or need more content? Drop a comment below, and let us know what topics you'd like to see next! Your support means the world to us. 😍