Recursion
A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. This technique is known as recursion.
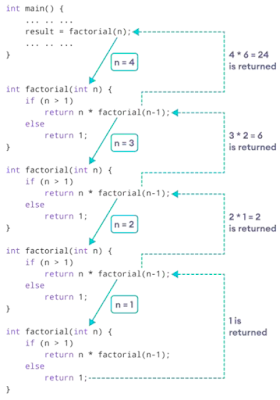
⭐Factorial of a Number:
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int factorial (int n){if(n>1){return n * factorial(n - 1);}else{return 1;}}int main(){int n, result;n = 4;result = factorial(n);cout << result;return 0;}
OUTPUT:
24
⭐Tower of Hanoi:
A few rules to be followed for Tower of Hanoi are:
- Only one disk can be moved among the towers at any given time.
- Only the 'top' disk can be removed.
- No large disk can sit over a small disk
- The minimal number of moves required to solve Tower of Hanoi puzzle of n disks would be (2^n) − 1.
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;void towerofHanoi(int n, char from_rod, char to_rod, char aux_rod){if (n==0){return;}towerofHanoi(n - 1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod);cout << "Move disk " << n << " from rod" << from_rod << " to rod " << to_rod << endl;towerofHanoi(n - 1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod);}int main(){int N=3;towerofHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B');return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Move disk 1 from rodA to rod C
Move disk 2 from rodA to rod B
Move disk 1 from rodC to rod B
Move disk 3 from rodA to rod C
Move disk 1 from rodB to rod A
Move disk 2 from rodB to rod C
Move disk 1 from rodA to rod C
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity:
- O(2N) There are two possibilities for every disk.
- Therefore, 2 * 2 * 2 * . . . * 2(N times) is 2N
Space Complexity:
- O(N), Function call Stack Space
⭐Merge Sort:
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Function to merge two halvesvoid merge(int A[], int start, int mid, int end) {int n1 = mid - start + 1;int n2 = end - mid;// Create temporary arraysint* left = new int[n1];int* right = new int[n2];// Copy data to temporary arraysfor (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)left[i] = A[start + i];for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++)right[j] = A[mid + 1 + j];// Merge the temporary arrays back into A[start..end]int i = 0;int j = 0;int k = start;while (i < n1 && j < n2) {if (left[i] <= right[j]) {A[k] = left[i];i++;} else {A[k] = right[j];j++;}k++;}// Copy the remaining elements of left[], if anywhile (i < n1) {A[k] = left[i];i++;k++;}// Copy the remaining elements of right[], if anywhile (j < n2) {A[k] = right[j];j++;k++;}// Free the temporary arraysdelete[] left;delete[] right;}// Merge Sort functionvoid merge_sort(int A[], int start, int end) {if (start < end) {int mid = (start + end) / 2;merge_sort(A, start, mid);merge_sort(A, mid + 1, end);merge(A, start, mid, end);}}// Function to print the arrayvoid printArray(int A[], int size) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)cout << A[i] << " ";cout << endl;}int main() {int A[] = {38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10};int size = sizeof(A) / sizeof(A[0]);cout << "Original array: ";printArray(A, size);merge_sort(A, 0, size - 1);cout << "Sorted array: ";printArray(A, size);return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Original array: 38 27 43 3 9 82 10
Sorted array: 3 9 10 27 38 43 82
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity:
- O(N log N), in all 3 cases (worst, average and best) as merge sort always divides the array into two halves and takes linear time to merge two halves.
Auxiliary Space:
- O(N), in merge sort, all elements are copied into an auxiliary array. So, N auxiliary space is required.
⭐Quick Sort:
CODE:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Function to partition the arrayint partition(int arr[], int low, int high, int pivot) {int i = low - 1;for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {if (arr[j] <= pivot) {i++;swap(arr[i], arr[j]);}}swap(arr[i + 1], arr[high]);return i + 1;}// Quick Sort functionvoid quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {if (low < high) {int pivot = arr[high];int pos = partition(arr, low, high, pivot);quickSort(arr, low, pos - 1);quickSort(arr, pos + 1, high);}}// Function to print the arrayvoid printArray(int arr[], int size) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)cout << arr[i] << " ";cout << endl;}int main() {int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);cout << "Original array: ";printArray(arr, size);quickSort(arr, 0, size - 1);cout << "Sorted array: ";printArray(arr, size);return 0;}
OUTPUT:
Original array: 10 7 8 9 1 5
Sorted array: 1 5 7 8 9 10
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity:
- Best Case: Ω (N log N)
- Average Case: θ ( N log N)
- Worst Case: O(N^2)
Auxiliary Space:
- O(1), if we don’t consider the recursive stack space. If we consider the recursive stack space, then, in the worst-case quick sort could make O(N).
🚨Thanks for visiting finenotes4u✨
Welcome to a hub for 😇Nerds and knowledge seekers! Here, you'll find everything you need to stay updated on education, notes, books, and daily trends.
💗 Bookmark our site to stay connected and never miss an update!
💌 Have suggestions or need more content? Drop a comment below, and let us know what topics you'd like to see next! Your support means the world to us. 😍